Difference between revisions of "IC Python API:List All Props"
Chuck (RL) (Talk | contribs) m (→Populating the Prop List) |
Chuck (RL) (Talk | contribs) m (→Building the UI) |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
== Building the UI == | == Building the UI == | ||
| − | Creating a window requires that we define it as a global entity and reference it in '''run_script''' definition. | + | Creating a window requires that we define it as a global entity and reference it in '''run_script''' definition. Notice that the window requires a main widget with a layout. The layout is also where individual child UI elements are added. |
<syntaxhighlight lang="Python"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="Python"> | ||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
dockable_window = RLPy.RUi.CreateRDockWidget() | dockable_window = RLPy.RUi.CreateRDockWidget() | ||
dockable_window.SetWindowTitle("All Scene Props") | dockable_window.SetWindowTitle("All Scene Props") | ||
| + | # Use wrapInstance to convert the dockable window to something that Python can understand, in this case a Dock Widget | ||
dock = wrapInstance(int(dockable_window.GetWindow()), | dock = wrapInstance(int(dockable_window.GetWindow()), | ||
QtWidgets.QDockWidget) | QtWidgets.QDockWidget) | ||
| Line 52: | Line 53: | ||
main_widget_layout.addWidget(combo_box) | main_widget_layout.addWidget(combo_box) | ||
| − | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Revision as of 23:05, 21 April 2019
- Main article: RL Python Samples.
This article will focus on creating a drop down list for all of the existing props in the current iClone scene.
Necessary Modules
Get started by loading the required modules for the script.
import RLPy
from PySide2 import QtWidgets
from PySide2.shiboken2 import wrapInstance
We'll need RLPy to access iClone's Python API and Pyside2 related modules to create a functional interface.
Qt Widgets
The Qt Widgets module extends Qt GUI with C++ widget functionality. This is the building blocks for composing the user interface.
Shiboken
The Shiboken module can be used to access internal information related to Pyside's binding technology. Access to this internal information is required to integrate Pyside with Qt based programs that offer Python scripting like iClone or just for debug purposes.
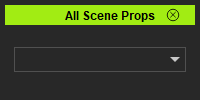
Building the UI
Creating a window requires that we define it as a global entity and reference it in run_script definition. Notice that the window requires a main widget with a layout. The layout is also where individual child UI elements are added.
# User Interface
dockable_window = None
def run_script():
global dockable_window
# Create an iClone Dock Widget
dockable_window = RLPy.RUi.CreateRDockWidget()
dockable_window.SetWindowTitle("All Scene Props")
# Use wrapInstance to convert the dockable window to something that Python can understand, in this case a Dock Widget
dock = wrapInstance(int(dockable_window.GetWindow()),
QtWidgets.QDockWidget)
main_widget = QtWidgets.QWidget()
dock.setWidget(main_widget)
main_widget_layout = QtWidgets.QVBoxLayout()
main_widget.setLayout(main_widget_layout)
combo_box = QtWidgets.QComboBox()
main_widget_layout.addWidget(combo_box)
If you run the above scripts, you'll receive an empty shell of an UI. Which is not very useful to us unless we populate the combo-box.
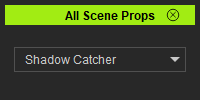
Populating the Prop List
We'll need some simple additional lines to populate the props list.
# Grab all props in the scene
all_props = RLPy.RScene.FindObjects(RLPy.EObjectType_Prop)
# Add an entry into the combo-box for every prop found
for i in range(len(all_props)):
combo_box.addItem(all_props[i].GetName())
Now when we run the script again, we get something that is much more useful.