Difference between revisions of "IC Python API:Transformation Key"
Chuck (RL) (Talk | contribs) m (→Loading a Test Prop) |
Chuck (RL) (Talk | contribs) m (→Animating the Box) |
||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
{{Single_Illustration|IClone_API_Transform_Key_01.png}} | {{Single_Illustration|IClone_API_Transform_Key_01.png}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Creating a Transformation Matrix == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Next, we'll need to create a transform object and fill it with scale, rotation, and translation information. The transform object is simply a 3x3 matrix where each transformational component occupies a row. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="Python"> | ||
| + | # Create a quaternion from euler angles | ||
| + | m3 = RLPy.RMatrix3().FromEulerAngle(RLPy.EEulerOrder_XYZ, 0, | ||
| + | 45 * RLPy.RMath.CONST_DEG_TO_RAD, 0)[0] | ||
| + | q_rotation = RLPy.RQuaternion().FromRotationMatrix(m3) | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Create a transform matrix | ||
| + | xform = RLPy.RTransform( | ||
| + | RLPy.RVector3(0.25, 0.25, 0.25), # Scale | ||
| + | q_rotation, # Rotation | ||
| + | RLPy.RVector3(100, 0, 100) # Translation | ||
| + | ) | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Notice that the second row of the transform matrix is occupied with a quaternion rotation. In order to input euler values, which is easier to understand by the layman, we must convert it to a rotational 3x3 matrix and convert that to a quaternion rotation. | ||
== Animating the Box == | == Animating the Box == | ||
Revision as of 17:58, 22 April 2019
- Main article: RL Python Samples.
This article focuses on animating a prop by keying its transformation. This is an alternative to the usual method of animating objects by setting data on transformational components like below:
data_block = prop.GetControl("Transform").GetDataBlock()
data_block.SetData("Position/PositionX", RLPy.RTime(0), RLPy.RVariant(100))
data_block.SetData("Position/PositionY", RLPy.RTime(0), RLPy.RVariant(0))
data_block.SetData("Position/PositionZ", RLPy.RTime(0), RLPy.RVariant(50))
Necessary Modules
Besides the RLPy standard module, we'll need two system based modules to load a prop from a directory with the likes of os and winreg
import RLPy
import os
import winreg
os
The os module provides a portable way of using operating system dependent functionality.
winreg
winreg offers functions that exposes the Windows registry API to Python.
Loading a Test Prop
Let's start by loading in a box object for the purpose of animation.
# Get the iClone 7 default template path
registry = winreg.ConnectRegistry(None, winreg.HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE)
rawKey = winreg.OpenKey(registry, r"SOFTWARE\Reallusion\iClone\7.0")
ic_template_path = os.path.abspath(
winreg.QueryValueEx(rawKey, "Template Data")[0])
# Load Box_001.iProp
RLPy.RFileIO.LoadFile(
ic_template_path + "//iClone Template//Props//3D Blocks//Box_001.iProp")
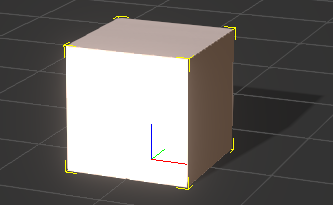
This gives us the following result:
Creating a Transformation Matrix
Next, we'll need to create a transform object and fill it with scale, rotation, and translation information. The transform object is simply a 3x3 matrix where each transformational component occupies a row.
# Create a quaternion from euler angles
m3 = RLPy.RMatrix3().FromEulerAngle(RLPy.EEulerOrder_XYZ, 0,
45 * RLPy.RMath.CONST_DEG_TO_RAD, 0)[0]
q_rotation = RLPy.RQuaternion().FromRotationMatrix(m3)
# Create a transform matrix
xform = RLPy.RTransform(
RLPy.RVector3(0.25, 0.25, 0.25), # Scale
q_rotation, # Rotation
RLPy.RVector3(100, 0, 100) # Translation
)
Notice that the second row of the transform matrix is occupied with a quaternion rotation. In order to input euler values, which is easier to understand by the layman, we must convert it to a rotational 3x3 matrix and convert that to a quaternion rotation.