Difference between revisions of "IC Python API:Basic Animation"
From Reallusion Wiki!
Chuck (RL) (Talk | contribs) m (→Parametric Algorithm) |
Chuck (RL) (Talk | contribs) m (→Setting up the Props) |
||
| Line 74: | Line 74: | ||
stick_db.SetData("Scale/ScaleZ", time, RLPy.RVariant(1.75)) | stick_db.SetData("Scale/ScaleZ", time, RLPy.RVariant(1.75)) | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Duo_Illustration | ||
| + | |Ic_python_api_basic_animation_01.png|The initial scene setup.| | ||
| + | |Ic_python_api_basic_animation_02.png|The result after running the script above.| | ||
| + | }} | ||
Revision as of 19:55, 12 May 2019
- Main article: RL Python Samples.
This article will focus on basic animation with the standard interface of setting the data bloc for the transform controller. However, we will attempt to spice it up with an algorithm for parametric animation.
Preparing the Scene
Prepare an iClone scene for this lesson with the following steps:
- Create a new iClone scene
- Create a ball: Create > Primitive Shape > Sphere.
- Create a cylinder: Create > Primitive Shape > Cylinder.
- Move the props apart for better visualization.
Required Modules
Only the standard RLPY module is required for this lesson.
import RLPy
Parametric Algorithm
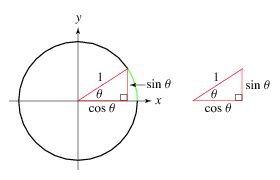
Parametric equations are commonly used to express the coordinates of the points that make up a geometric object such as a curve or surface. In this example, we'll use the following formula to travel along the parameter of a circle:
point.x = origin.x + radius * Cosine( angle )
point.y = origin.y + radius * Sine( angle )
- ⚠ Angle is in radians.
Point on Parameter
def parametric_point(center_point, radius, angle):
# Convert angle to radians
a = RLPy.RMath.CONST_DEG_TO_RAD * angle
# Calculate the point on the circumference of a circle
x = center_point.x + radius * RLPy.RMath.Cos(a)
y = center_point.y + radius * RLPy.RMath.Sin(a)
return RLPy.RVector2(x, y)
Setting up the Props
Let's change the way the props are displayed before deploying animation keys.
# Grab the ball in the scenes: Create > Primitive Shape > Sphere
ball = RLPy.RScene.FindObject(RLPy.EObjectType_Prop, "Ball_000")
# Grab the stick in the scenes: Create > Primitive Shape > Cylinder
stick = RLPy.RScene.FindObject(RLPy.EObjectType_Prop, "Cylinder")
# Get transform control and data block for the ball
ball_control = ball.GetControl("Transform")
ball_control.ClearKeys()
ball_db = ball_control.GetDataBlock()
# Get transform control and data block for the stick
stick_control = stick.GetControl("Transform")
stick_control.ClearKeys()
stick_db = stick_control.GetDataBlock()
# Setup the stick that spins by laying it on its side and extending its length
time = RLPy.RTime(0)
stick_db.SetData("Position/PositionZ", time, RLPy.RVariant(35))
stick_db.SetData("Rotation/RotationY", time, RLPy.RVariant(90 * rad))
stick_db.SetData("Scale/ScaleX", time, RLPy.RVariant(0.25))
stick_db.SetData("Scale/ScaleY", time, RLPy.RVariant(0.25))
stick_db.SetData("Scale/ScaleZ", time, RLPy.RVariant(1.75))
 The initial scene setup.
The initial scene setup.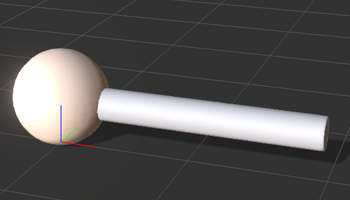 The result after running the script above.
The result after running the script above.