Difference between revisions of "IC Python API:Progress Bar"
From Reallusion Wiki!
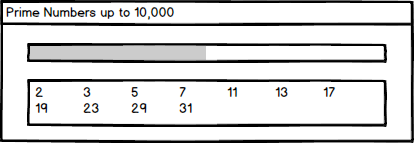
Chuck (RL) (Talk | contribs) (Created page with "{{TOC}} {{Parent|IC_Python_API:RL_Python_Samples|RL Python Samples}} File:Ic_python_api_prime_number_01.png This lesson will go over the creation of a progress bar as on...") |
Chuck (RL) (Talk | contribs) m |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
This lesson will go over the creation of a progress bar as one of the fundamental building blocks of a functional user interface. | This lesson will go over the creation of a progress bar as one of the fundamental building blocks of a functional user interface. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Required Modules == | ||
| + | |||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="Python"> | ||
| + | import RLPy | ||
| + | from PySide2 import QtWidgets | ||
| + | from PySide2.shiboken2 import wrapInstance | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Prime Number Checker == | ||
| + | |||
| + | For our CPU intensive operation, we'll be checking for prime numbers from 1 to 10,000. A prime number is natural number greater than 1 that cannot be formed by multiplying two smaller natural numbers. The opposite of this is a composite number. For example, 5 is prime because the only ways of writing it as a product, 1 × 5 or 5 × 1, involve 5 itself. However, 6 is composite because it is the product of two numbers (2 × 3) that are both smaller than 6. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="Python"> | ||
| + | def check_prime_number(num): | ||
| + | if num > 1: # Prime numbers are greater than 1 | ||
| + | for i in range(2, num): # Check for factors | ||
| + | if (num % i) == 0: | ||
| + | return False | ||
| + | else: | ||
| + | return True | ||
| + | else: # If input number is less than or equal to 1, it is not prime | ||
| + | return False | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Building the UI == | ||
| + | |||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="Python"> | ||
| + | window = RLPy.RUi.CreateRDockWidget() | ||
| + | window.SetWindowTitle("All Prime Numbers (0-10K)") | ||
| + | |||
| + | dock = wrapInstance(int(window.GetWindow()), QtWidgets.QDockWidget) | ||
| + | dock.setFixedSize(350, 350) | ||
| + | dock.setStyleSheet( | ||
| + | """ QProgressBar{ font: bold; color: black; border: 1px solid black; background-color: grey;} | ||
| + | QProgressBar::chunk { width: 1px; background-color: #13c1ec}""") | ||
| + | |||
| + | widget = QtWidgets.QWidget() | ||
| + | dock.setWidget(widget) | ||
| + | |||
| + | layout = QtWidgets.QVBoxLayout() | ||
| + | widget.setLayout(layout) | ||
| + | |||
| + | progress_bar = QtWidgets.QProgressBar() | ||
| + | |||
| + | text_edit = QtWidgets.QTextEdit(readOnly=True) | ||
| + | |||
| + | button = QtWidgets.QPushButton("Calculate") | ||
| + | button.clicked.connect(run) | ||
| + | |||
| + | for widget in [progress_bar, text_edit, button]: | ||
| + | layout.addWidget(widget) | ||
| + | |||
| + | window.Show() | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Notice the '''Calculate''' button runs a function to start the entire prime number search process which is covered below. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Running the Script == | ||
| + | |||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="Python"> | ||
| + | def run(): | ||
| + | |||
| + | progress_bar.setRange(1, 10000) | ||
| + | button.setHidden(True) | ||
| + | found = 0 | ||
| + | |||
| + | for i in range(1, 10001): | ||
| + | if check_prime_number(i): | ||
| + | text_edit.insertPlainText("{:,}".format(i) + "\t") | ||
| + | found += 1 | ||
| + | progress_bar.setValue(i) | ||
| + | progress_bar.setFormat(f"Calculating: {round(i/100)}%") | ||
| + | bottom = text_edit.verticalScrollBar().maximum() | ||
| + | text_edit.verticalScrollBar().setValue(bottom) | ||
| + | |||
| + | progress_bar.setFormat(f"{ '{:,}'.format(found) } prime numbers found.") | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Everything Put Together == | ||
| + | |||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="Python"> | ||
| + | import RLPy | ||
| + | from PySide2 import QtWidgets | ||
| + | from PySide2.shiboken2 import wrapInstance | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | def check_prime_number(num): | ||
| + | if num > 1: # Prime numbers are greater than 1 | ||
| + | for i in range(2, num): # Check for factors | ||
| + | if (num % i) == 0: | ||
| + | return False | ||
| + | else: | ||
| + | return True | ||
| + | else: # If input number is less than or equal to 1, it is not prime | ||
| + | return False | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | def run(): | ||
| + | |||
| + | progress_bar.setRange(1, 10000) | ||
| + | button.setHidden(True) | ||
| + | found = 0 | ||
| + | |||
| + | for i in range(1, 10001): | ||
| + | if check_prime_number(i): | ||
| + | text_edit.insertPlainText("{:,}".format(i) + "\t") | ||
| + | found += 1 | ||
| + | progress_bar.setValue(i) | ||
| + | progress_bar.setFormat(f"Calculating: {round(i/100)}%") | ||
| + | bottom = text_edit.verticalScrollBar().maximum() | ||
| + | text_edit.verticalScrollBar().setValue(bottom) | ||
| + | |||
| + | progress_bar.setFormat(f"{ '{:,}'.format(found) } prime numbers found.") | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | window = RLPy.RUi.CreateRDockWidget() | ||
| + | window.SetWindowTitle("All Prime Numbers (0-10K)") | ||
| + | |||
| + | dock = wrapInstance(int(window.GetWindow()), QtWidgets.QDockWidget) | ||
| + | dock.setFixedSize(350, 350) | ||
| + | dock.setStyleSheet( | ||
| + | """ QProgressBar{ font: bold; color: black; border: 1px solid black; background-color: grey;} | ||
| + | QProgressBar::chunk { width: 1px; background-color: #13c1ec}""") | ||
| + | |||
| + | widget = QtWidgets.QWidget() | ||
| + | dock.setWidget(widget) | ||
| + | |||
| + | layout = QtWidgets.QVBoxLayout() | ||
| + | widget.setLayout(layout) | ||
| + | |||
| + | progress_bar = QtWidgets.QProgressBar() | ||
| + | |||
| + | text_edit = QtWidgets.QTextEdit(readOnly=True) | ||
| + | |||
| + | button = QtWidgets.QPushButton("Calculate") | ||
| + | button.clicked.connect(run) | ||
| + | |||
| + | for widget in [progress_bar, text_edit, button]: | ||
| + | layout.addWidget(widget) | ||
| + | |||
| + | window.Show() | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Revision as of 19:21, 27 May 2019
- Main article: RL Python Samples.
This lesson will go over the creation of a progress bar as one of the fundamental building blocks of a functional user interface.
Required Modules
import RLPy
from PySide2 import QtWidgets
from PySide2.shiboken2 import wrapInstance
Prime Number Checker
For our CPU intensive operation, we'll be checking for prime numbers from 1 to 10,000. A prime number is natural number greater than 1 that cannot be formed by multiplying two smaller natural numbers. The opposite of this is a composite number. For example, 5 is prime because the only ways of writing it as a product, 1 × 5 or 5 × 1, involve 5 itself. However, 6 is composite because it is the product of two numbers (2 × 3) that are both smaller than 6.
def check_prime_number(num):
if num > 1: # Prime numbers are greater than 1
for i in range(2, num): # Check for factors
if (num % i) == 0:
return False
else:
return True
else: # If input number is less than or equal to 1, it is not prime
return False
Building the UI
window = RLPy.RUi.CreateRDockWidget()
window.SetWindowTitle("All Prime Numbers (0-10K)")
dock = wrapInstance(int(window.GetWindow()), QtWidgets.QDockWidget)
dock.setFixedSize(350, 350)
dock.setStyleSheet(
""" QProgressBar{ font: bold; color: black; border: 1px solid black; background-color: grey;}
QProgressBar::chunk { width: 1px; background-color: #13c1ec}""")
widget = QtWidgets.QWidget()
dock.setWidget(widget)
layout = QtWidgets.QVBoxLayout()
widget.setLayout(layout)
progress_bar = QtWidgets.QProgressBar()
text_edit = QtWidgets.QTextEdit(readOnly=True)
button = QtWidgets.QPushButton("Calculate")
button.clicked.connect(run)
for widget in [progress_bar, text_edit, button]:
layout.addWidget(widget)
window.Show()
Notice the Calculate button runs a function to start the entire prime number search process which is covered below.
Running the Script
def run():
progress_bar.setRange(1, 10000)
button.setHidden(True)
found = 0
for i in range(1, 10001):
if check_prime_number(i):
text_edit.insertPlainText("{:,}".format(i) + "\t")
found += 1
progress_bar.setValue(i)
progress_bar.setFormat(f"Calculating: {round(i/100)}%")
bottom = text_edit.verticalScrollBar().maximum()
text_edit.verticalScrollBar().setValue(bottom)
progress_bar.setFormat(f"{ '{:,}'.format(found) } prime numbers found.")
Everything Put Together
import RLPy
from PySide2 import QtWidgets
from PySide2.shiboken2 import wrapInstance
def check_prime_number(num):
if num > 1: # Prime numbers are greater than 1
for i in range(2, num): # Check for factors
if (num % i) == 0:
return False
else:
return True
else: # If input number is less than or equal to 1, it is not prime
return False
def run():
progress_bar.setRange(1, 10000)
button.setHidden(True)
found = 0
for i in range(1, 10001):
if check_prime_number(i):
text_edit.insertPlainText("{:,}".format(i) + "\t")
found += 1
progress_bar.setValue(i)
progress_bar.setFormat(f"Calculating: {round(i/100)}%")
bottom = text_edit.verticalScrollBar().maximum()
text_edit.verticalScrollBar().setValue(bottom)
progress_bar.setFormat(f"{ '{:,}'.format(found) } prime numbers found.")
window = RLPy.RUi.CreateRDockWidget()
window.SetWindowTitle("All Prime Numbers (0-10K)")
dock = wrapInstance(int(window.GetWindow()), QtWidgets.QDockWidget)
dock.setFixedSize(350, 350)
dock.setStyleSheet(
""" QProgressBar{ font: bold; color: black; border: 1px solid black; background-color: grey;}
QProgressBar::chunk { width: 1px; background-color: #13c1ec}""")
widget = QtWidgets.QWidget()
dock.setWidget(widget)
layout = QtWidgets.QVBoxLayout()
widget.setLayout(layout)
progress_bar = QtWidgets.QProgressBar()
text_edit = QtWidgets.QTextEdit(readOnly=True)
button = QtWidgets.QPushButton("Calculate")
button.clicked.connect(run)
for widget in [progress_bar, text_edit, button]:
layout.addWidget(widget)
window.Show()