Difference between revisions of "IC Python API:Spring Joints"
Chuck (RL) (Talk | contribs) m (→Required Files) |
Chuck (RL) (Talk | contribs) m (→Usage Instructions) |
||
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
== Usage Instructions == | == Usage Instructions == | ||
| + | #Clone or download the Reallusion/iClone GitHub. | ||
| + | #Copy '''SpringJoints''' folder into the iClone install directory > '''...\Bin64\OpenPlugin'''. | ||
| + | #Load the script into the project from the menu: '''Plugins > Python Samples > Spring Joints'''. | ||
#Load or create a scene with Props attached in a hierarchical order. | #Load or create a scene with Props attached in a hierarchical order. | ||
#Load the '''Spring Bones''' script and select the desired joints in the Bones tree list view. | #Load the '''Spring Bones''' script and select the desired joints in the Bones tree list view. | ||
Latest revision as of 02:29, 11 March 2020
- Main article: RL Python Samples.
Demo Video
Description
Spring Joints allows you to apply spring physics to designated bone and prop hierarchies in the scene. The spring effect is calculated using an algorithm that takes into account several physics elements such as stiffness, bounciness, and damping. This script is versatile and can turn any existing bone or prop hierarchy into an active physics spring chain. You can also create a prop chain by attaching various props together and apply spring physics using this plugin.
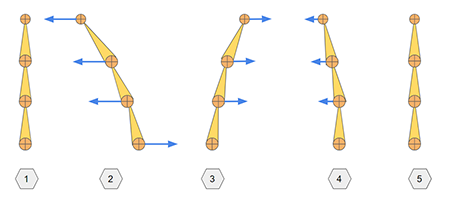 iClone's native spring implementation acts like a lagging chain.
iClone's native spring implementation acts like a lagging chain.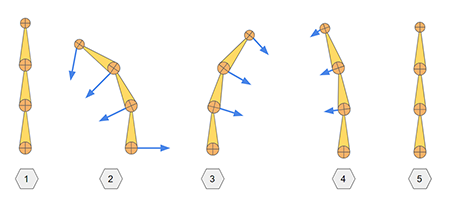 Spring Bones script also takes into account joint rotations.
Spring Bones script also takes into account joint rotations.
Course Prerequisites
You should familiarize yourself with the following fundamental articles before you proceed:
| Link | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Transform Math | Access recipes for 3D transformational math dealing with spatial calculations. |
| Rotation Math | Access recipes for 3D rotational math dealing with spatial calculations. |
| Error Handling | Learn to handle and debug show-stopping errors in code. |
| Handling Time | Learn to manage complex timeline features by making a special re-usable class. |
| Basic Math | Access recipes for basic mathematics for common numerical operations. |
Takeaway Lessons
- Apply spring physics to bones or attached props.
- Create a tree list view to represent bone hierarchies.
- Update UI by receiving callback events.
- Using Timer events.
Required Files
- Sample project.
- Spring Joints Python script.
- Spring Extensions Python script.
You can download this plugin from the Reallusion Marketplace.
To acquire and view the source code, please visit Reallusion GitHub.
Usage Instructions
- Clone or download the Reallusion/iClone GitHub.
- Copy SpringJoints folder into the iClone install directory > ...\Bin64\OpenPlugin.
- Load the script into the project from the menu: Plugins > Python Samples > Spring Joints.
- Load or create a scene with Props attached in a hierarchical order.
- Load the Spring Bones script and select the desired joints in the Bones tree list view.
- Adjust the Stiffness, Bounciness, and Dampness settings:
- Stiffness: how rigid are the joints?
- Bounciness: how likely will the joints swing back and forth?
- Dampness: how fast do the joints come to a complete stop?
- You could use the [Start Simulation] button to test the spring parameters and using[Stop Simulation] to stop it.
- After you are satisfied with your settings, click the [ Apply Setting ] button and watch the bone chain swing around as the objects moves.
- You could use [Clear Key] to remove the result.
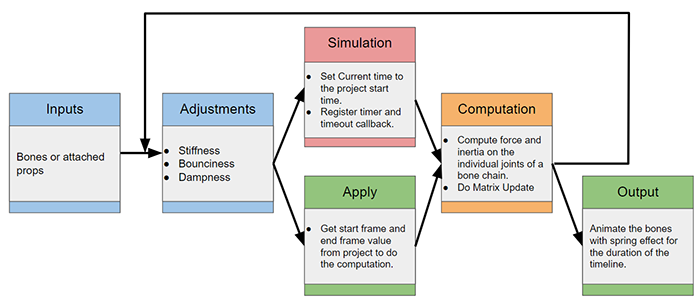
Code Flow
APIs Used
You can research the following references for the APIs deployed in this code.
main.py
- RLPy.RPyTimerCallback.__init__()
- RLPy.REventCallback.__init__()
- RLPy.RDialogCallback.__init__()
- RLPy.REventHandler.UnregisterCallback()
- RLPy.RVector3()
- RLPy.RMatrix4()
- RLPy.RQuaternion()
- RLPy.RMath.ACos()
- RLPy.RMath.AlmostZero()
- RLPy.RMath.CONST_PI) or RLPy.RMath.AlmostZero()
- RLPy.RUi.GetMainWindow()
- RLPy.RUi.AddMenu()
- RLPy.REventHandler.RegisterCallback()
- RLPy.RGlobal.SetTime()
- RLPy.RPyTimer()
- RLPy.RGlobal.Play()