Difference between revisions of "IC Python API:File Path"
Chuck (RL) (Talk | contribs) (Created page with "{{TOC}} {{Parent|IC_Python_API:RL_Python_Samples|RL Python Samples}} === Required Modules === Besides the rudimentary Reallusion Python API, we'll need to use Qtwidgets to b...") |
Chuck (RL) (Talk | contribs) m (→Everything Put Together) |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{TOC}} | {{TOC}} | ||
| − | {{Parent|IC_Python_API | + | {{Parent|IC_Python_API#Python_of_the_Month|Python of the Month}} |
| − | + | Oftentimes, you'll need to handle external files in the form of loading, writing and reading. This article will go over doing just that with Python scripting. | |
| + | |||
| + | == Required Modules == | ||
Besides the rudimentary Reallusion Python API, we'll need to use Qtwidgets to build our user interface and shiboken2 to convert the dialog window to something Python can understand. | Besides the rudimentary Reallusion Python API, we'll need to use Qtwidgets to build our user interface and shiboken2 to convert the dialog window to something Python can understand. | ||
| Line 12: | Line 14: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | == User Interface == | |
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Ic_python_api_file_path_01.png|frame]] | ||
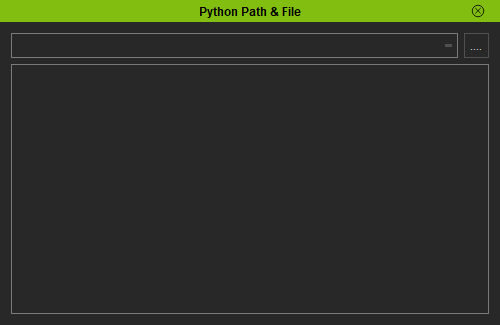
We'll need to create a user interface with a line at the top that shows the directory location, a button for opening the file browse dialog, and a text input to display the contents of the file. | We'll need to create a user interface with a line at the top that shows the directory location, a button for opening the file browse dialog, and a text input to display the contents of the file. | ||
| Line 34: | Line 38: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | == File Dialog Request == | |
Next we'll need a definition for the file dialog procedure to populate the directory field and the contents text field. | Next we'll need a definition for the file dialog procedure to populate the directory field and the contents text field. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="python"> | ||
| + | def open_file(): | ||
| + | file_path = RLPy.RUi.OpenFileDialog("Python Files(*.py)") | ||
| + | |||
| + | if len(file_path) > 0: | ||
| + | pathText.setPlainText(file_path[0]) | ||
| + | f = open(file_path[0], "r") | ||
| + | contentText.setPlainText(f.read()) | ||
| + | f.close() | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | button.clicked.connect(open_file) | ||
| + | |||
| + | window.Show() | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Using QT only === | ||
| + | |||
| + | This was the previous code for open file dialog. It's been deprecated for Reallusion's more convenient API and kept here for posterity. | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="python"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="python"> | ||
| Line 56: | Line 80: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | === Everything Put Together == | + | {{Images2 |
| + | |image1=Ic_python_api_file_path_03.png | ||
| + | |image2=Ic_python_api_file_path_02.png | ||
| + | |caption1= File request dialog is a standard Window's file browser. Notice that we are restricting the search to '''.py''' files with the filter attribute. | ||
| + | |caption2= The top field is populated with the file location and the bottom field for the contents of the file. | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Everything Put Together == | ||
| + | |||
| + | You can copy and paste the following code into a PY file and load it into iClone via '''Script > Load Python'''. | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang= "python"> | <syntaxhighlight lang= "python"> | ||
| Line 81: | Line 114: | ||
def open_file(): | def open_file(): | ||
| − | + | file_path = RLPy.RUi.OpenFileDialog("Python Files(*.py)") | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | if | + | if len(file_path) > 0: |
| − | pathText.setPlainText( | + | pathText.setPlainText(file_path[0]) |
| − | f = open( | + | f = open(file_path[0], "r") |
contentText.setPlainText(f.read()) | contentText.setPlainText(f.read()) | ||
f.close() | f.close() | ||
| Line 97: | Line 128: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | === APIs Used === | |
You can research the following references for the APIs deployed in this code. | You can research the following references for the APIs deployed in this code. | ||
Latest revision as of 22:17, 19 October 2020
- Main article: Python of the Month.
Oftentimes, you'll need to handle external files in the form of loading, writing and reading. This article will go over doing just that with Python scripting.
Required Modules
Besides the rudimentary Reallusion Python API, we'll need to use Qtwidgets to build our user interface and shiboken2 to convert the dialog window to something Python can understand.
import RLPy
from PySide2 import QtWidgets
from PySide2.shiboken2 import wrapInstance
User Interface
We'll need to create a user interface with a line at the top that shows the directory location, a button for opening the file browse dialog, and a text input to display the contents of the file.
window = RLPy.RUi.CreateRDialog()
window.SetWindowTitle("Python Path & File")
dialog = wrapInstance(int(window.GetWindow()), QtWidgets.QDialog)
dialog.setFixedWidth(500)
layout = QtWidgets.QHBoxLayout()
dialog.layout().addLayout(layout)
pathText = QtWidgets.QPlainTextEdit(readOnly=True, maximumHeight=25)
contentText = QtWidgets.QPlainTextEdit(minimumHeight=250)
button = QtWidgets.QPushButton("....", minimumHeight=25, minimumWidth=25)
layout.addWidget(pathText)
layout.addWidget(button)
dialog.layout().addWidget(contentText)
File Dialog Request
Next we'll need a definition for the file dialog procedure to populate the directory field and the contents text field.
def open_file():
file_path = RLPy.RUi.OpenFileDialog("Python Files(*.py)")
if len(file_path) > 0:
pathText.setPlainText(file_path[0])
f = open(file_path[0], "r")
contentText.setPlainText(f.read())
f.close()
button.clicked.connect(open_file)
window.Show()
Using QT only
This was the previous code for open file dialog. It's been deprecated for Reallusion's more convenient API and kept here for posterity.
def open_file():
file_dialog = QtWidgets.QFileDialog()
file_dialog.setNameFilter("*.py")
file_dialog.exec()
if(len(file_dialog.selectedFiles()) > 0):
pathText.setPlainText(file_dialog.selectedFiles()[0])
f = open(file_dialog.selectedFiles()[0], "r")
contentText.setPlainText(f.read())
f.close()
button.clicked.connect(open_file)
window.Show()
-
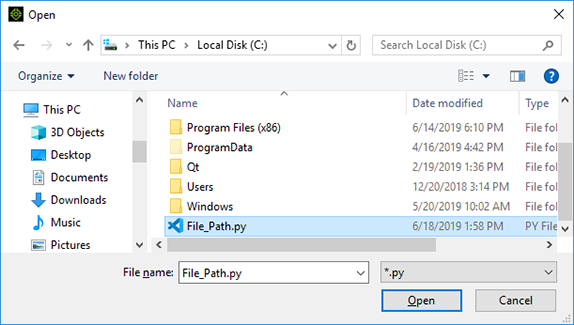 File request dialog is a standard Window's file browser. Notice that we are restricting the search to .py files with the filter attribute.
File request dialog is a standard Window's file browser. Notice that we are restricting the search to .py files with the filter attribute. -
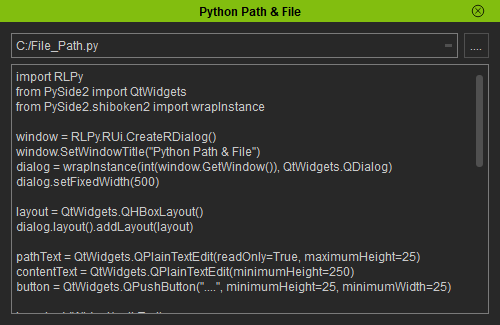 The top field is populated with the file location and the bottom field for the contents of the file.
The top field is populated with the file location and the bottom field for the contents of the file.
Everything Put Together
You can copy and paste the following code into a PY file and load it into iClone via Script > Load Python.
import RLPy
from PySide2 import QtWidgets
from PySide2.shiboken2 import wrapInstance
window = RLPy.RUi.CreateRDialog()
window.SetWindowTitle("Python Path & File")
dialog = wrapInstance(int(window.GetWindow()), QtWidgets.QDialog)
dialog.setFixedWidth(500)
layout = QtWidgets.QHBoxLayout()
dialog.layout().addLayout(layout)
pathText = QtWidgets.QPlainTextEdit(readOnly=True, maximumHeight=25)
contentText = QtWidgets.QPlainTextEdit(minimumHeight=250)
button = QtWidgets.QPushButton("....", minimumHeight=25, minimumWidth=25)
layout.addWidget(pathText)
layout.addWidget(button)
dialog.layout().addWidget(contentText)
def open_file():
file_path = RLPy.RUi.OpenFileDialog("Python Files(*.py)")
if len(file_path) > 0:
pathText.setPlainText(file_path[0])
f = open(file_path[0], "r")
contentText.setPlainText(f.read())
f.close()
button.clicked.connect(open_file)
window.Show()
APIs Used
You can research the following references for the APIs deployed in this code.