Difference between revisions of "IC Python API:Using Pyside2 For Creating User Interface"
From Reallusion Wiki!
Chuck (RL) (Talk | contribs) m |
Chuck (RL) (Talk | contribs) m (→Creating a Simple iClone Dialog Window) |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
The following simple example shows how to obtain a handle for the PySide application object and create a dialog window: | The following simple example shows how to obtain a handle for the PySide application object and create a dialog window: | ||
| − | + | <syntaxhighlight lang="Python"> | |
import PySide2, RLPy | import PySide2, RLPy | ||
from PySide2 import * | from PySide2 import * | ||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
sample_dialog.Show() | sample_dialog.Show() | ||
| − | </ | + | </syntaxhighlight> |
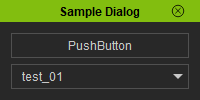
{{Single_Illustration|Python_api_sample_dialog_01.png}} | {{Single_Illustration|Python_api_sample_dialog_01.png}} | ||
Revision as of 00:20, 9 April 2019
- Main article: iClone Python API.
iClone ships with a pre-built version of PySide 2.0 compatible with Python 3.6.2. This version includes all standard PySide2 modules.
Creating a Simple iClone Dialog Window
The following simple example shows how to obtain a handle for the PySide application object and create a dialog window:
import PySide2, RLPy
from PySide2 import *
from PySide2.shiboken2 import wrapInstance
#-- Make a global variable contain dialog --#
sample_dialog = None
def run_script():
global sample_dialog
sample_dialog = RLPy.RUi.CreateRDialog()
sample_dialog.SetWindowTitle("Sample Dialog")
#-- Create Pyside layout for RDialog --#
pyside_dialog = wrapInstance(int(sample_dialog.GetWindow()), QtWidgets.QDialog)
pyside_dialog.setFixedWidth(200)
sample_layout = pyside_dialog.layout()
#-- Add PushButton --#
pushbutton = QtWidgets.QPushButton("PushButton")
sample_layout.addWidget(pushbutton)
#-- Add ComboBox --#
combobox = QtWidgets.QComboBox()
combobox.addItem("test_01")
combobox.addItem("test_02")
sample_layout.addWidget(combobox)
sample_dialog.Show()
Loading and Editing a Qt Designer UI Widget
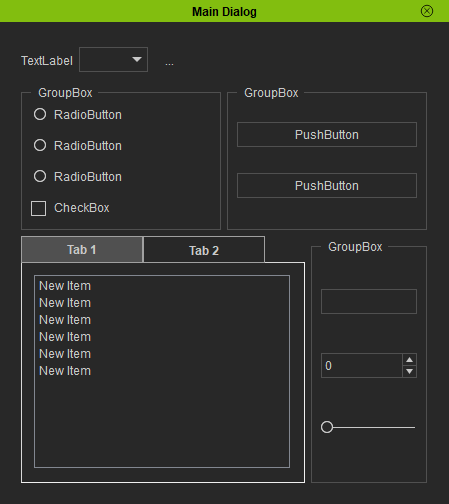
This sample demonstrates how to load a Qt Designer UI file and edit the loaded widgets. You must first use Qt Designer to create a *.ui file that represents the widget tree.
Code:
import PySide2, RLPy, os
from PySide2 import *
from PySide2.shiboken2 import wrapInstance
#-- Make a global variable contain Dialog --#
sample_dialog = None
qtui_widget = None
def run_script():
global sample_dialog
#-- Make the RL Dialog --#
sample_dialog = RLPy.RUi.CreateRDialog()
sample_dialog.SetWindowTitle("Main Dialog")
#-- Wrap to PySide Dialog --#
pyside_dialog = wrapInstance(int(sample_dialog.GetWindow()), QtWidgets.QDialog)
sample_layout = pyside_dialog.layout()
#-- Load Ui file --#
ui_file = QtCore.QFile(os.path.dirname(__file__) + "/sample.ui")
ui_file.open(QtCore.QFile.ReadOnly)
qtui_widget = QtUiTools.QUiLoader().load(ui_file)
ui_file.close()
#-- Assign the Ui file to PySide dialog --#
sample_layout.addWidget(qtui_widget)
sample_dialog.Show()