IC Python API:Align to Camera
From Reallusion Wiki!
- Main article: RL Python Samples.
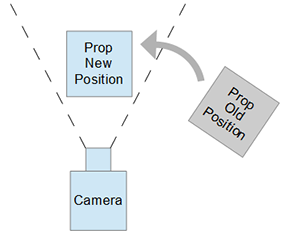
This article will go over a script that can align props in front of the current camera based on a user defined distance. We will go over using transform matrix calculations required to position and rotate world-space objects into transform space locations and orientations.
Required Modules
Besides the fundamental Reallusion Python module, we'll also need Pyside2 and os to read the QT UI file and build the user interface.
import RLPy
import os
from PySide2 import *
from PySide2.shiboken2 import wrapInstance
Align to Camera Function
def align_to_camera():
items = RLPy.RScene.GetSelectedObjects()
if len(items) > 0:
if items[0].GetType() == RLPy.EObjectType_Prop:
camera = RLPy.RScene.GetCurrentCamera()
camera_transform = camera.WorldTransform()
transform_matrix = camera_transform.Matrix()
offset_matrix = RLPy.RMatrix4()
offset_matrix.MakeIdentity()
offset_matrix.SetTranslate(RLPy.RVector3(0, 0, -widget.distance.value()))
transform_matrix = offset_matrix * transform_matrix
new_transform = RLPy.RTransform()
new_transform.From(transform_matrix)
transform_control = items[0].GetControl("Transform")
transform_control.SetValue(RLPy.RGlobal.GetTime(), new_transform)
Creating the UI
We'll need to load the configured QT UI file. You can download Align_to_Camera.ui here -make sure this UI file is placed in the same script directory.
window = RLPy.RUi.CreateRDialog()
window.SetWindowTitle("Align Prop to Camera")
dialog = wrapInstance(int(window.GetWindow()), QtWidgets.QDialog)
dialog.setFixedWidth(350)
qt_ui_file = QtCore.QFile(os.path.dirname(__file__) + "/Align_to_Camera.ui")
qt_ui_file.open(QtCore.QFile.ReadOnly)
widget = QtUiTools.QUiLoader().load(qt_ui_file)
qt_ui_file.close()
dialog.layout().addWidget(widget)
widget.pushButton.clicked.connect(align_to_camera)
window.Show()
Everything Put Together
You can copy and paste the following code into a PY file and load it into iClone via Script > Load Python.
import RLPy
import os
from PySide2 import *
from PySide2.shiboken2 import wrapInstance
def align_to_camera():
items = RLPy.RScene.GetSelectedObjects()
if len(items) > 0:
if items[0].GetType() == RLPy.EObjectType_Prop:
camera = RLPy.RScene.GetCurrentCamera()
camera_transform = camera.WorldTransform()
transform_matrix = camera_transform.Matrix()
offset_matrix = RLPy.RMatrix4()
offset_matrix.MakeIdentity()
offset_matrix.SetTranslate(RLPy.RVector3(0, 0, -widget.distance.value()))
transform_matrix = offset_matrix * transform_matrix
new_transform = RLPy.RTransform()
new_transform.From(transform_matrix)
transform_control = items[0].GetControl("Transform")
transform_control.SetValue(RLPy.RGlobal.GetTime(), new_transform)
window = RLPy.RUi.CreateRDialog()
window.SetWindowTitle("Align Prop to Camera")
dialog = wrapInstance(int(window.GetWindow()), QtWidgets.QDialog)
dialog.setFixedWidth(350)
qt_ui_file = QtCore.QFile(os.path.dirname(__file__) + "/Align_to_Camera.ui")
qt_ui_file.open(QtCore.QFile.ReadOnly)
widget = QtUiTools.QUiLoader().load(qt_ui_file)
qt_ui_file.close()
dialog.layout().addWidget(widget)
widget.pushButton.clicked.connect(align_to_camera)
window.Show()
APIs Used
You can research the following references for the APIs deployed in this code.