Difference between revisions of "IC Python API:Camera Auto-Focus"
From Reallusion Wiki!
Chuck (RL) (Talk | contribs) m (→Usage Instructions) |
Chuck (RL) (Talk | contribs) m (→Takeaway Lessons) |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
*Calculate single axis distance between two object (useful for finding Z-depth). | *Calculate single axis distance between two object (useful for finding Z-depth). | ||
| − | * | + | *Creating and setting camera DOF keys. |
| − | * | + | *Deploy timer and handling timer callbacks. |
== Required Files == | == Required Files == | ||
Revision as of 19:17, 23 September 2019
- Main article: RL Python Samples.
Demo Video
Description
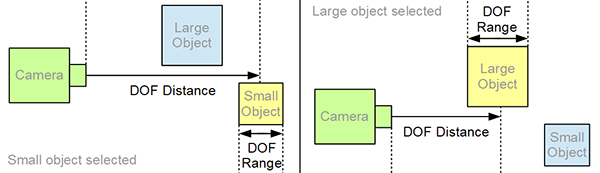
Auto-Focus can be used to automatically calculate the DOF (Depth of Field) distance and range for the current camera according to the viewing distance of a selected object. This script operates and updates in near real-time.
Course Prerequisites
You should familiarize yourself with the following fundamental articles before you proceed:
Takeaway Lessons
- Calculate single axis distance between two object (useful for finding Z-depth).
- Creating and setting camera DOF keys.
- Deploy timer and handling timer callbacks.
Required Files
- Auto-focus Python script
- iClone scene with select-able props or characters.
Usage Instructions
- Clone or download the Reallusion/iClone GitHub.
- Copy Camera_Auto_Focus folder into the iClone install directory > ...\Bin64\OpenPlugin.
- Load the script into the project from the menu: Plugins > Python Samples > Camera Auto-Focus.
- Follow the instructions in the subsequent dialog window.
Code Flow
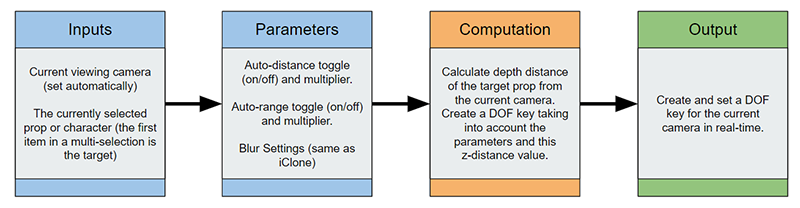
- The current viewing camera is the currently driven camera.
- The current selection is the DOF target, the first item in multiple selection is designated as the target.
- Adjust the parameters such as Auto-Distance and Auto-Range toggle and multiplier.
- The z-distance between the target prop from the current viewing camera is calculated.
- DOF key is created taking into account the depth distance value and the parameter settings.
- The created DOF key is set on the current viewing camera in near real-time.
APIs Used
You can research the following references for the APIs deployed in this code.
main.py
- RLPy.RMatrix4()
- RLPy.REventCallback.__init__()
- RLPy.RPyTimerCallback.__init__()
- RLPy.RDialogCallback.__init__()
- RLPy.REventHandler.UnregisterCallback()
- RLPy.RScene.GetCurrentCamera()
- RLPy.RScene.GetSelectedObjects()
- RLPy.RVector3()
- RLPy.RKey()
- RLPy.RGlobal.GetTime()
- RLPy.RPyTimer()
- RLPy.REventHandler.RegisterCallback()
- RLPy.RUi.CreateRDockWidget()
- RLPy.RUi.GetMainWindow()
- RLPy.RUi.AddMenu()